What is Yttrium? Electron configuration, Symbol
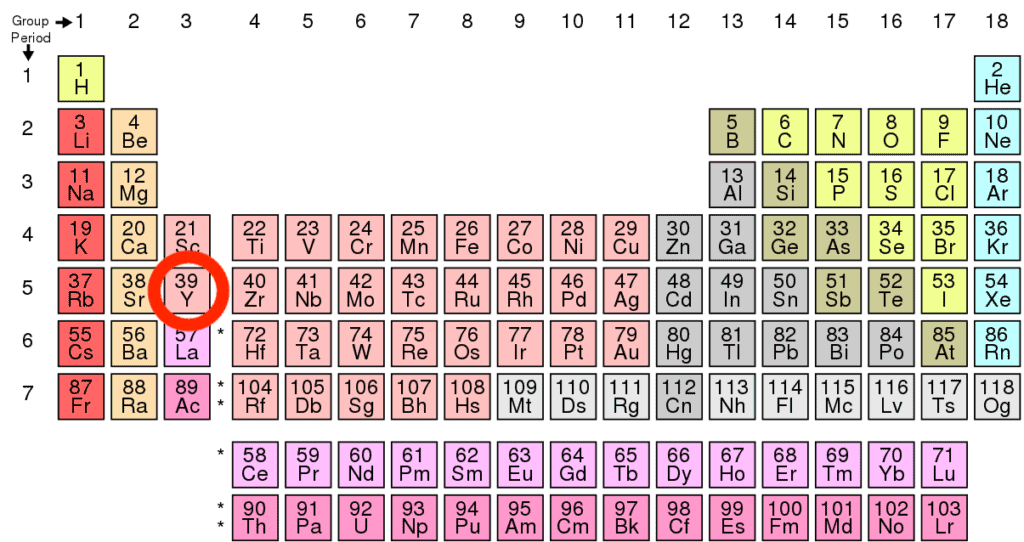
Yttrium is a chemical element with the number 39 in the Periodic Table of the Elements. Metallic in appearance, yttrium is gray and soft. Chemical behavior of Yttrium is close to lanthanides and historically classified as a rare earth.
|
General information of Yttrium element |
|
|
Yttrium Symbol |
Y |
|
Atomic number of Yttrium |
39 |
|
Family |
Transition metal |
|
Group |
3 |
|
Period |
5 |
|
Block |
d |
|
Volumic mass |
4.469 g.cm-3 |
|
Color |
Silvery white |
|
Atomic properties of Yttrium |
|
|
Atomic mass of Yttrium |
88.90584 u |
|
Yttrium Atomic radius |
180 pm |
|
Electronic configuration of Yttrium |
[Kr] 5s² 4d¹ |
|
Electrons by energy level |
2 | 8 | 18 | 9 | 2 |
|
Oxide |
Weak base |
|
Physical properties of Yttrium |
|
|
Ordinary state |
Solid |
|
Melting point of Yttrium |
1522 ° C |
|
Boiling point |
3345 ° C |
A little history of Yttrium element
Etymology
The name of element 39, yttrium, was chosen as a tribute to the village of ytterby (Village in Sweden) where the ore in which this element was discovered was mined.
Discovery of Yttrium
It all began in 1789 when a Finnish chemist bearing the name of Johan Gadolin identified a new oxide in a sample of gadolinite, called ytterbite at the time. This rock had been discovered two years earlier by Lieutenant Carl Axel Arrhenius near the Swedish village of Ytterby and its work was confirmed in 1797 by Anders Gustaf Ekeberg who decided to name this new oxide yttria.
Who discovered yttrium?
Johan Gadolin is a Finnish chemist who lived between 1760 and 1852. He is known to have been the first to discover a chemical element belonging to the rare earth family: yttrium. The mineral gadolinite and the chemical element gadolinium were named in his honor.
Electronic configuration of Yttrium:
Yttrium electron configuration can be written as-
- Detailed electronic configuration of Yttrium element: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 1
- Short notation of electronic configuration of Yttrium: [Kr] 5s 2 4d 1
The yttrium atom and Zr +1 , Tc +4 have the same electronic configuration.
Important points about Yttrium element
- Yttrium atoms in compounds have oxidation states 3, 2.
- Y3+ , Y2+ are Ions of Yttrium.
- Yttrium atoms in compounds exhibit valence III, II.
Presence of Yttrium
Yttrium is a chemical element that can be found naturally in the environment, very often in association in minerals with rare earths but also in uranium ore.
Having in the Earth's crust is a relatively abundant element, it is indeed the 28th most abundant element with a Clarke 31 ppm.
Yttrium can be present in different minerals such as:
- Monazite sands, of formula (Ce, La, Th, Nd, Y) PO 4
- Bastnäsite, of formula (Ce, La, Th, Nd, Y) (CO 3 ) F
- Allanite, orthite
- Samarkite
- And gadolinite
**Please note, these minerals are considered to be radioactive.
Physical and chemical properties of Yttrium
Yttrium as a simple body
It is a silvery and shiny metal which, on contact with dioxygen, oxidizes on the surface and is covered with a layer of yttrium oxide. It reacts with water as well as with most acids and bases forming dihydrogen and yttrium ions.
Yttrium ions in aqueous solution
The yttrium III ion, of formula Y3+ , is a monatomic cation having a defect of three electrons. It can be formed when metallic yttrium reacts with water or with an acid.
Yttrium-based compounds
Yttrium oxide, formula Y2 O3 , is a mineral also called yttria which is generally in the form of a white powder.
It forms naturally on the surface of metallic yttrium when the latter is in contact with oxygen.
Isotopes of Yttrium
Yttrium has 33 isotopes known to date. Their mass numbers vary from 76 to 108. Among all these isotopes, only yttrium 89 is stable, which therefore makes it a monoisotopic and mononucleosis element.
The radioisotope with the smallest half-life is yttrium 76 with a half-life of 500 ns while the one with the longest half-life is yttrium 91 with a half-life of 58 days.
Yttrium Uses
- Yttrium is used in different fields, but one of its main uses is in making red phosphors for cathode ray screens.
- In addition, iron and yttrium garnets are used as microwave filters. Other uses of Yttrium you can see as YAG (Yttrium Garnet Aluminum), imitate diamonds in jewelry. Apart from these Yttrium can also be used in the manufacturing of lasers emitting (an infrared light mainly used in medicine).
- But, when it is in additive form, the use of yttrium is quite different. Indeed, it can be used to deoxidize vanadium, while yttrium 90 is used in cancer treatments.
- Present in certain superconductors such as YBaCuO, it allows the latter to have a critical temperature above the boiling point of nitrogen.
Toxicity of Yttrium element
It is important to handle yttrium with care as it can be dangerous. This is because yttrium vapors and gases can cause pulmonary embolism. This risk is all the more increased if the exposure becomes prolonged.
In general, yttrium, like other rare earth metals with comparable properties, accumulates in the liver when absorbed.
FAQS
What is the atomic radius of Yttrium?
The atomic radius of the Yttrium element is 180 pm, here pm means picometer i.e. (picometer = 10-12 m). Also the Covalent radius is 190±7 pm.
What is the melting point of Yttrium?
The melting point of the yttrium is 1522°C (2772°F, 1795 K), whereas the boiling point is 3345°C.
What is the valency of Yttrium?
As you know, the atomic number of yttrium elements is 39 so this element has trivalency, i.e. its valency is three.
Know about more periodic elements- Aluminium, Gadolinium, Germanium, Neon, Oxygen, Potassium, Promethium, Selenium, Sodium, Terbium, Tellurium, Yttrium, Ytterbium, Zirconium
Related Articales
Recently Posted
-
भगवान गौतम बुद्ध जीवन परिचय | Gautam Buddha in Hindi
December 15, 2022. -
कार्बन के अपररूप Allotropes of Carbon in Hindi
November 5, 2022. -
मिश्र धातु किसे कहते हैं? उपयोग, नाम, गुण Alloy in Hindi
July 27, 2022. -
गलनांक किसे कहते हैं? परिभाषा, उदाहरण Melting Point in Hindi
July 20, 2022. -
परिमाप किसे कहते हैं? Perimeter in Hindi
July 19, 2022.