What is RFID?
What is RFID?
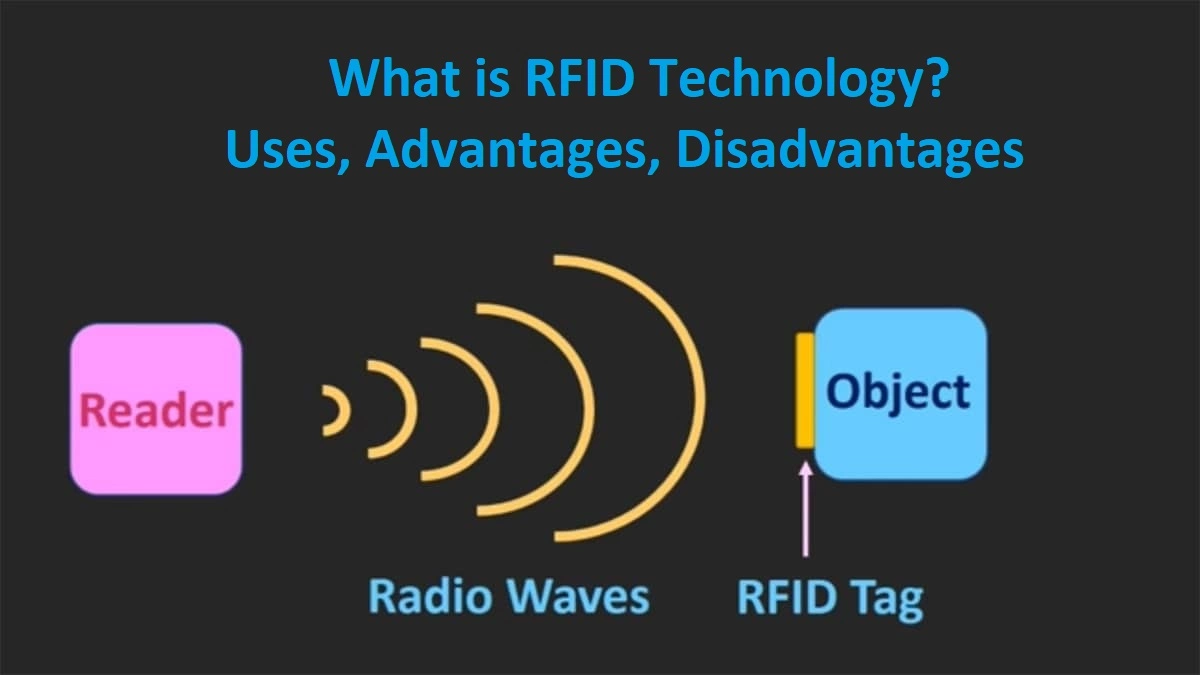
RFID (Full Form: Radio-Frequency IDentification ) is understood to mean a transfer technology based on electromagnetic waves, promoting contactless data exchange within transmission / reception systems.
How does RFID technology work?
RFID systems consist of at least one RFID reader and a large number of RFID transponders which primarily function as mobile storage media for data. There is also a need for a computer capable of interpreting the data that has been entered.
The data transfer is done without contact, quite simply in the air. We are therefore talking about an air interface between sender and recipient. The composition of the basic technical elements, the spectrum of functions, as well as the frequencies of use employed depend very much on the type of RFID technology and its field of application.
Structure of an RFID reader
An RFID reader is a technological device that emits either a short range alternating magnetic field or high frequency radio waves. Everything will depend on the type of device and its field of application.
If an RFID transponder passes into the electromagnetic field of the reader, a connection is established with the reader making it possible to read the RFID transponder. The reading process is managed by software installed on the reader. This software is generally provided with interfaces allowing communication with other computer systems. Depending on the type of device, it is possible to describe the transponder, and you will be able to modify the information stored on the chip.
Modern RFID readers are able to read multiple transponders simultaneously. This ability to read several transponders at the same time appears to be the main advantage of RFID technology over other methods of object identification, such as for example barcode identification.
To enable RFID readers to be able to communicate with several tags at the same time, different anti-collision methods have been developed, in which transponders are assigned, for example, different access times or specific frequencies. This makes it possible to avoid the stacking of signals.
Structure of an RFID transponder
An RFID transponder is a radio communication device capable of picking up an incoming signal and responding to it automatically. The word transponder is a combination of the English words Transmitter and Responder .
The smallest transponders are only a few millimeters long. A distinction is made between the following three types of transponders:
- passive
- active
- semi-active
The basic elements that make up an RFID transponder are an electronic chip and an antenna (which usually takes the form of a coil). The electronic chip of an ordinary transponder offers a recording capacity of a few bytes to several kilobytes, depending on the model chosen.
Depending on the type of need, you may have a recording capacity which is sufficient to enter a series of a few digits allowing the chip to be uniquely identified, or a larger capacity to store the equivalent of several typed pages of text.
Associated with an antenna which is printed, glued or soldered, the RFID chip constitutes what is called the inlay. The inlay is ultra-sensitive and not very resistant. This is why we will generally laminate an RFID inlay.
For example on a self-adhesive label (Smart Label): these are the RFID tags ( standing for “label”). If the transponder must be able to withstand heavy loads, it is possible to integrate the electronics in a plastic card or in a badge.
If it is a passive or semi-active transponder , the RFID chip does not emit any electromagnetic field. Rather, it is the alternate field of the reader which is modified to allow the transfer of the data read. Active transponders have their own transmitter.
- The RFID transponders liabilities have no power source, and can under no circumstances issue any autonomously signal. The chip of a passive transponder is supplied with temporary power by means of a capacitor (usually integrated) at the time of connection with the reader. In most cases, the coupling is done by induction.
- Both active and semi-active RFID transponders have their own power supply in the form of a small battery, so they are a bit larger. In the case of passive RFID transponders, data transfer is limited to a few meters. Active and semi-active transponders increase the range of an RFID system by several hundred meters. The connection is made either by induction or by electromagnetism.
RFID frequencies
The most common RFID systems use transmission frequencies from the ISM frequency bands that are free of rights. They can be used free of charge and without any authorization in industrial applications at high frequencies, in the scientific and medical sector, and even in the domestic field.
RFID systems are distinguished by the frequency range they use:Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), Ultra-high Frequency (UHF) and Super-high Frequency (SHF). These different frequency ranges have very different ranges and transfer speeds. There is no international RFID standard for prescribing specific frequencies.
- Low Frequency, LF: Low frequency RFID systems emit long waves located in the frequency range from 125 kHz to 135 kHz. Reading distances are significantly less than one meter. The transfer rate is relatively low. RFID systems with a frequency of 125 kHz are generally used in application areas such as production, assembly, access control and animal identification. Passive RFID transponders, using a low frequency range, are supplied with energy by induction.
- HF-RFID High Frequency, HF (high frequencies) systems use short waves with a frequency of 6.78 MHz, 13.56 MHz or 27.125 MHz and are distinguished by their high transfer rate. The maximum reading or writing distance is 3 meters. HF transponders have antennas with fewer turns. This makes it possible to reduce its size. For smart labels used in logistics, the frequency 13.56 MHz is used by default, worldwide.
- Ultra-high Frequency, UHF (ultra high frequency) RFID systems in the UHF frequency range also allow very good range and excellent transfer speed. The maximum reading or writing distance is 10 meters. When using systems with active transponders, ranges of 100 meters can be achieved. Due to the short wavelength, a simple dipole will suffice as an antenna. In Europe, the standard value used for the frequency of UHF transponders is 868 MHz. The frequency usually used in the United States is 915 MHz, but it is not allowed in RFID systems in Europe. Walls of buildings, objects and other obstacles help to significantly reduce and reflect UHF waves.
- Super-high Frequency, SHF (microwave): In RFID technology, ISM bands are also used with frequencies of 2.45 GHz and 5.8 GHz in the microwave range. SHF RFID systems are distinguished by their very high transfer rate. The range of a passive SHF transponder can go up to 3 meters, a distance which can reach 300 meters if you opt for active transponders. As with UHF waves, microwaves can be severely hampered by physical obstacles.
The table below gives you an overview of the frequency bands used in the different RFID systems, as well as their properties.
| Low frequencies | High frequencies | Very high frequencies (passive / active) | Microwave (passive / active) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency range | Less than 135 kHz | 13.56 MHz | 868 MHz (EU), 915 MHz (US) | 2.45 GHz, 5.8 GHz |
| Reading distance | Less than 1 meter | Up to 3 meters | Up to 10 or even 100 meters | Up to 3 or even 300 meters |
| Type of connection between reader and transponder | Induction (near field) | Induction (near field) | Electromagnetic (far field) | Electromagnetic (far field) |
| Transfer rate | Weak | Raised | Raised | Very high |
| Disturbance by liquids | Weak | Weak | Very high | Very high |
| Disturbance by metals | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Necessary orientation of the transponder | No | No | Partially | Always |
| ISO / IEC standards | 11784/85 and 14223 | 14443, 15693 and 18000 | 14443, 15693 and 18000 | 18000 |
| Supports for the transponder chip (examples) | Glass injections, Plastic cases, Chip card, Smart label | Smart label, Industrial Transponder | Smart label, Industrial transponder | Large format transponder |
| Application domain | Access and routing control, Immobilizer, Laundry, Gas meter, Animal identification | Laundry, Ticketing, Tracking & traceability, Simultaneous entry of several tags | Stock, Logistics Pallet registration, Container traceability | Vehicle identification, road tolls |
| Acceptance | Whole world | Whole world | EU / United States | Not accepted in the EU |
Coupling
The coupling between a reader and a transponder is generally carried out in one of the following ways.
- Close coupling : the close coupling system is always implemented so that the maximum distance between the reader and the transponder does not exceed one centimeter. This is in principle possible in all frequency ranges. The transfer is then generally done by induction. Such systems are used in particular in sectors with a high level of safety requirements. Among the areas of use, it is worth mentioning contactless payment or authentication by locking systems. Due to the short distance, one can be satisfied with passive transponders.
- Remote pairing : the remotely coupled system allows data transfer at a distance of up to one meter. Here, too, the connection is usually made by induction. Frequencies used are usually 135 kHz (LF) or 13.56 MHz (HF). Passive transponders are also used for remote couplings. This transfer method is very suitable for use in warehouses and in the field of logistics.
- Long-range systems : Long-range RFID systems typically operate over an ultra-high frequency range (868 MHz or 915 MHz) and provide a read / write distance of several hundred meters. Long range systems are only under development in the microwave RFID industry. To promote the best possible range, there are active RFID transponders with their own power supply. Long-range RFID systems are particularly popular for vehicle identification, especially for road tolls.
Write and read functions
The basic principle of an RFID system is to identify a transponder by reading its unique identifier. For more complex uses, modifiable transponders can be used. In this context, there are three types of transponders (labels):
- Read-only: RFID transponders are defined once and for all by the manufacturer, and can then be read as often as you like. It is no longer possible to add, replace or delete information.
- Write once, read many : WORM transponders are delivered blank by the manufacturer. The user can then enter there once and for all the data he wishes. These can be read several times.
- Read and write: RFID transponders in this category are rewritable. The content of these transponders can be edited, deleted and rewritten multiple times, with lots of write and read access. On this type of transponder, it is also possible to restrict write access.
Different RFID transponders can have various additional functions, depending on their type and design.
RFID tags equipped with a “Kill-Code” can be permanently deactivated upon receipt of a well-defined signal. This functionality is used, among other things, to secure the merchandise with RFID, thus preventing the possibility of consulting and reading the articles equipped with transponders, once they have left the sales area.
If confidential information is stored on RFID chips, such as access codes for locking systems or bank data, it is possible to add data encryption .
There are also means of programming the transponder chips so that the reading of data is subject to a secret password. Such transponders will in this case check the identity of the reader before granting him access to the read memory.
Uses of RFID Technology
RFID technology in everyday life
Today, RFID systems are primarily used in logistics and retail. The possibilities of use also concern production, management of stocks and goods, identification of vehicles, the fight against counterfeiting and the marking of livestock.
Consumers are also faced with RFID technology when using card payment systems. It is also common to find RFID transponders installed in working time recording systems, and in electronic locking systems. Certain RFID chips are also integrated into new identity cards or new passports and allow the identification of people.
Logistics
In the logistics industry, RFID technology can replace barcodes. RFID transponders allow clear identification of goods throughout the distribution chain and thus promote transparent monitoring of the flow of goods.
The main fields of application are traceability, identification of objects and location of goods. The inventory industry stands to gain from implementing RFID-based processes. This is also the case for container management and quality control.
For example in monitoring the cold chain. Remotely coupled systems are common. In this case, the transponders are installed directly on the packaging or on the transport pallet. Reading is done using small hand-held "scanners" or sensors, usually placed in door frames or on the tips of forklifts.
Inventory and item management
RFID tags have found their place not only in retail, but also in libraries, where they play an important role in product and inventory management. The advantage of RFID technology, compared to other more traditional entry systems, is the possibility of being able to use the simultaneous entry of several RFID tags..
This system is used, for example, when returning books to libraries. This simultaneous entry makes it possible, for example, to identify all the books stacked on a table at once, without having to scan each book individually.
Supermarkets also have an interest in relying on RFID systems, for example to better manage the flow of goods, for restocking, to monitor products whose consumption date is about to be exceeded. These techniques have not yet made a real breakthrough in the retail sector, in particular for reasons of legislation and data protection.
Securing the goods
In retail, RFID systems are used for merchandise management but also for product security . RFID technology has gained the most ground in the textile industry. RFID transponders are incorporated by sewing or some other method in the garments in the form of flexible labels.
For product security, RFID tags are typically added to products already during the manufacturing process. They are therefore discreet, efficient and more economical than other electronic locks.
Data protection authorities, however, remain critical of RFID merchandise management systems, among other things because the chips embedded in products continue to be readable by the customer after purchasing the product.
Production
The use of RFID systems in production concerns as much the traceability of products and materials as the automation of production chains .
The use of RFID technology is not only aimed at speeding up manufacturing processes, but also improving safety at workstations and controlling the quality of production.
The idea is to provide each product (or product component) with a chip allowing unambiguous identification, but also containing information on manufacture, assembly, maintenance and recycling. RFID technology, associated with the IoT (Internet of Things) is one of the basic elements that make up the Smart Factory in the vision of Industry 4.0.
Vehicle identification
A possible application of the long-range RFID system is the identification of vehicles, for example in the context of access control, road tolls, speed controls, car-sharing offers or parking management.
One could consider number plates with RFID chip (IDePlates) as a replacement or in addition to current license plates. In this way, we can use the RFID chip to regulate the filling at the service station or the toll by simply passing in front of a terminal.
Counterfeiting and commercial piracy
RFID technology can be used to combat commercial hacking or help supplement other security measures, such as optical holograms or serial numbers. For example, there is labelingconsisting of discretely integrating passive RFID transponders into products at the time of their production.
Such labels make it possible to unambiguously identify branded products throughout the distribution chain, and to check the authenticity of an item if necessary. If you have installed an RFID system capable of reading a large number of tags simultaneously, you will be able to perform quick verification even in a large batch of goods.
To prevent any falsification of the information stored on the transponder chip, it is advisable to use encryption methods. It is also conceivable that the consumer can carry out this check himself, for example with his smartphone.
Animal identification
The identification of livestock is also a sector in which RFID transponders find their place, particularly in the form of chips implanted directly under the skin, and which allow the identification of livestock or pets. RFID technology here makes it possible to replace necklaces or ear loops .
Payment cards
RFID is also the technology behind contactless means of payment, by electronic chip or Smart Device. For security reasons, the data transfer takes place within the framework of a close coupling. The communication near-field Near Field Communication (NFC) has become the international standard for data transfer. Among the main users of NFC contactless technology are Apple Pay, Google Pay etc
**Note
The coupling method employed by NFC in RFID systems is a special method designed by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) in conjunction with the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). The centralized standards are ISO / IEC 18092, 21481 and 14443..
Time recording
RFID systems designed to record working hours are also widely used, for example replacing card time clock systems . Instead of clocking in when arriving at work, the employee simply presents his transponder in front of a terminal when he arrives, when he leaves, at the start and at the end of the break.
The data is then interpreted in the background by a computer system, and recorded as an hourly balance or deficit in its hour account. Sport also uses RFID systems to record times. For example, transponders are installed on athletes' shoes, on bicycles or racing cars, to record the crossing of the finish line with extreme precision.
Permission and access controls
Presented in the form of key rings or smart cards, RFID transponders allow identification in electronic locking systems . This type of access control has a considerable advantage compared to all systems using keys.
If an employee loses their transponder, all they have to do is lock their ID. This avoids the costly replacement of a lock, which is often necessary in the event of loss of key. One can perfectly envision RFID security checks with user identification to allow someone to access a workstation, machines, tools, or even a vehicle.
Identification of persons
Identity documents can also be equipped with RFID technology, which would facilitate easier reading of personal data .
In identity cards, such a chip has been integrated for several years. In the future, one can also consider implanting such an identification chip directly under the skin of a person. This chip could contain not only identification data, but also medical data , such as the existence of certain allergies, intolerances, medical history or drugs.
Advantages and disadvantages of RFID technology
The advantages and disadvantages of RFID systems are generally discussed in comparison to other means of contactless identification. Most of the fields of application mentioned above can replace RFID systems with other visual identification means, for example, for reading a barcode or a QR code. In this context, RFID technology has the following advantages and disadvantages:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Contactless data transfer (even without eye contact) | Disruption of radio transfer by liquids and metals (depending on the frequency used) |
| Possibility of opting for a large reading / writing distance (depending on the material chosen) | Still very little standardized (especially internationally) |
| Fast transfer rate possible (depending on the material chosen) | Transparency and data protection |
| Read / write access possible through certain materials (such as wood and cardboard) | Unlike barcodes, RFID transponders can only be read with a technical device (reader). |
| Simultaneous reading of several RFID chips possible | |
| Reduced wear / Particularly strong depending on the substrate | |
| Encryption possibilities | |
| Rewritable on some models |
What we have coverred in this article:-
- What is RFID?
- How does RFID technology work?
- Use of RFID technology in everyday life
- Advantages and disadvantages of RFID technology
Related Articales
Recently Posted
-
भगवान गौतम बुद्ध जीवन परिचय | Gautam Buddha in Hindi
December 15, 2022. -
कार्बन के अपररूप Allotropes of Carbon in Hindi
November 5, 2022. -
मिश्र धातु किसे कहते हैं? उपयोग, नाम, गुण Alloy in Hindi
July 27, 2022. -
गलनांक किसे कहते हैं? परिभाषा, उदाहरण Melting Point in Hindi
July 20, 2022. -
परिमाप किसे कहते हैं? Perimeter in Hindi
July 19, 2022.